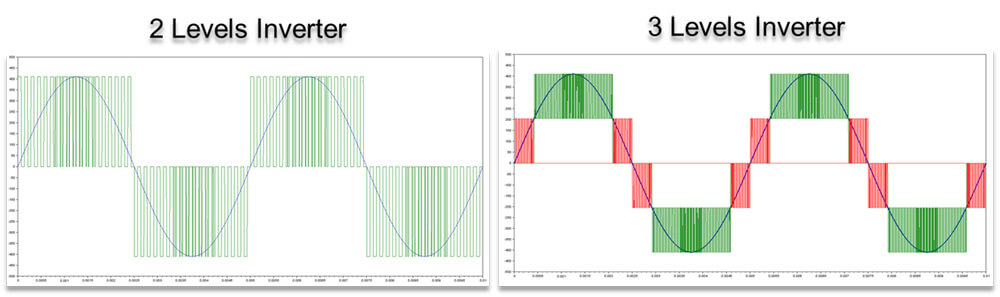
RPFM Modulator
The RPFM Modulator is a space-vector modulator, capable of operating across the full sinusoidal linear region and extending into the space-vector region.
Additionally, the RPFM modulator can operate outside the linear zone with partial or full saturation (six-step mode).
The main characteristics of the 2-level RPFM modulator are:
- output transitions occur at fixed time units, guaranteeing a minimum ON/OFF pulse to the power stage
- operation with either all 8 vectors or only 7 vectors; using 8 vectors minimizes switch commutations
- no more than one output phase changes per time unit
- DC-link voltage is evaluated at each fixed time unit
The 3-level RPFM modulator is an extension of the 2-level version with the following characteristics:
- generation of 27 vectors
- requires a T-type NPC topology in the power stage
Switching between 2-level and 3-level modes (and vice versa) can be performed on the fly according to operating conditions.
In both 2- and 3-level modes, the time-unit (minimum pulse width) configuration can also be changed on the fly.
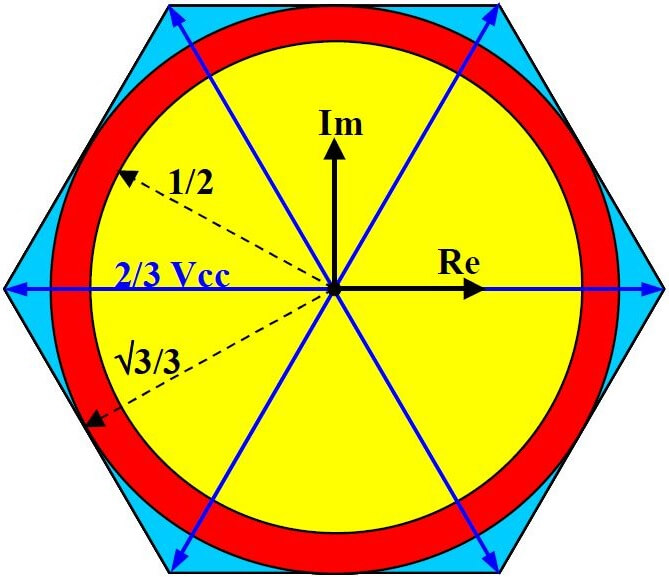
Sinusoidal reference A sinusoidal modulator transfers a voltage equal to DC_LINK / 2 to the motor.
Assuming this value corresponds to 100%, space-vector modulation extends to 115.47% = 2 / √3.
A saturated sine wave reaches 127.324% = 4 / π.
Space-vector reference A space-vector modulator transfers (2/3) · DC_LINK to the motor.
Assuming the space-vector value as 100%, the sine wave is lower at 86.603% = √3 / 2.
A saturated sine wave extends to 110.266% = 2√3 / π.